A Schengen Visa is a type of visa that allows individuals to travel to and within the Schengen Area, which consists of 26 European countries. The Schengen Area operates as a single jurisdiction for international travel purposes, with no border controls between participating countries.
The Schengen Visa is issued by the embassy or consulate of the country where the traveler intends to spend the majority of their time. The visa allows the holder to travel freely within the Schengen Area for a period of up to 90 days within a 180-day period.
To apply for a Schengen Visa, applicants must provide proof of their travel plans, such as flight reservations and accommodations, as well as proof of financial means to support themselves during their stay. They must also provide documentation demonstrating their intention to return to their home country, such as proof of employment or enrollment in a school.
It's important to note that not all countries in the European Union are part of the Schengen Area, and some countries outside the EU are part of the Schengen Area. It's always best to check with the embassy or consulate of the country you intend to visit to determine whether a Schengen Visa is required.
Who Needs a Visa to Enter Europe?
The visa requirements for entering Europe depend on several factors, such as the traveler's nationality, the purpose of their trip, and the duration of their stay. Generally speaking, citizens of the European Union (EU) and the European Economic Area (EEA) do not need a visa to enter any other EU or EEA country. However, citizens of non-EU/EEA countries may need a visa to enter Europe.
The following is a general overview of visa requirements for entering Europe:
- Citizens of the European Union and European Economic Area: Citizens of EU and EEA countries can travel freely within the EU and EEA without a visa.
- Visa-free countries: Citizens of some non-EU/EEA countries can travel to Europe without a visa for short stays of up to 90 days. The list of visa-free countries includes the United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and many others. However, it's important to check the latest visa requirements for your country before you travel.
- Schengen Visa: Citizens of non-EU/EEA countries who are not visa-exempt may need to apply for a Schengen Visa if they plan to travel to any of the 26 Schengen Area countries for a short stay of up to 90 days. This visa allows travelers to move freely between the participating countries within the Schengen Area.
- National Visas: Citizens of non-EU/EEA countries who wish to stay in a single EU/EEA country for a longer period, such as to study or work, may need to apply for a national visa. This type of visa is issued by the individual country where the traveler intends to stay and is usually valid for up to one year.
It's important to note that visa requirements can change, so it's always best to check with the embassy or consulate of the country you intend to visit to determine whether a visa is required for your specific situation.
Travel Documents and Entry Requirements for non-EU Nationals
The travel documents and entry requirements for non-EU nationals can vary depending on the country they plan to visit. However, there are some general guidelines that can be followed:
- Passport: Non-EU nationals will need a valid passport to enter most countries. The passport should be valid for at least six months from the date of entry.
- Visa: Non-EU nationals may need a visa to enter some countries. The type of visa required can depend on the purpose of the trip, the length of the stay, and the country being visited. It's important to check with the embassy or consulate of the country you plan to visit for specific visa requirements.
- Travel insurance: Some countries require non-EU nationals to have travel insurance as a condition of entry. This is to ensure that visitors have access to medical care in case of illness or injury during their stay.
- Vaccinations: Some countries require non-EU nationals to have certain vaccinations before they can enter. It's important to check with the embassy or consulate of the country you plan to visit for specific vaccination requirements.
- Entry requirements: Some countries may require non-EU nationals to show proof of funds or a return ticket as a condition of entry. It's important to check with the embassy or consulate of the country you plan to visit for specific entry requirements.
Overall, it's important for non-EU nationals to do their research and check the entry requirements for the country they plan to visit well in advance of their trip. This will help ensure a smooth and hassle-free entry into the country.
Which European Countries issue Schengen Visas?
The Schengen Area is a group of 26 European countries that have abolished passport and other types of border control at their common borders, allowing for free and unrestricted movement of people within the area. These countries issue Schengen visas:
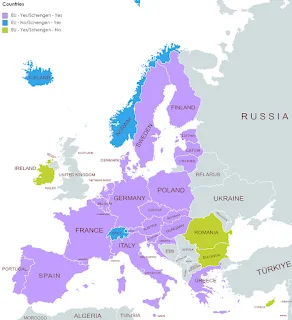 |
| Which European Countries issue Schengen Visas? |
- Austria
- Belgium
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
These countries have agreed to issue a common visa, called the Schengen visa, which allows visitors to enter any of these countries without the need for additional visas or border checks within the Schengen Area. It's important to note that not all European countries are part of the Schengen Area, and some countries within the area have specific requirements or restrictions on certain types of travelers.
Schengen Visa Types for Short-Term Visits in Europe
There are several types of Schengen visas for short-term visits to Europe, including:
- Uniform Schengen Visas (USV): These visas allow travelers to enter any of the 26 Schengen countries for up to 90 days within a 180-day period. They are issued for tourism, business, or visiting family or friends.
- Limited Territorial Validity (LTV) Visas: These visas are issued for a specific Schengen country or countries and allow travelers to stay in that country or countries for up to 90 days within a 180-day period.
- National Visas: These visas are issued by a specific Schengen country and allow travelers to stay in that country for longer than 90 days, typically for work, study, or family reunification purposes.
- Airport Transit Visa (ATV): This visa is required for travelers who are not entering the Schengen Area but are passing through a Schengen country's international transit area on their way to a destination outside the Schengen Area.
It's important to note that the specific requirements and application procedures for each type of Schengen visa may vary slightly by country. Applicants should carefully review the requirements and procedures for the country where they will be applying.
How Long Does the Schengen Visa Allow Me to Stay in Europe?
The Schengen visa allows you to stay in the Schengen Area for up to 90 days within a 180-day period. This means that you can enter and exit the Schengen Area as many times as you like within the 180-day period, but you must not stay for more than 90 days in total.
The 180-day period is calculated as a rolling period, which means that the calculation is not based on a fixed calendar year or six-month period. Instead, it is calculated by looking back at the previous 180 days from the date of your entry into the Schengen Area. During this period, you can stay for a maximum of 90 days in total, regardless of how many times you enter or exit the Schengen Area.
It's important to note that overstaying your visa can have serious consequences, including being banned from entering the Schengen Area in the future. Therefore, it's important to carefully plan your travel and ensure that you do not stay beyond the allowed 90 days within a 180-day period.
How to Apply for a Visa to Enter Europe?
The process for applying for a visa to enter Europe can vary depending on the country you plan to visit and your individual circumstances. However, here are some general steps to follow:
- Determine the type of visa you need: Depending on the purpose of your visit, you may need a short-stay Schengen visa, a long-stay visa, a student visa, a work visa, or another type of visa. Check with the embassy or consulate of the country you plan to visit to determine the type of visa you need.
- Gather required documents: The required documents for a visa application can vary by country, but typically include a valid passport, a completed visa application form, a recent passport-size photo, proof of travel arrangements (such as flight tickets), proof of accommodation, proof of sufficient funds for your stay, and possibly other supporting documents, such as a letter of invitation or proof of employment or enrollment in a school.
- Schedule an appointment: Contact the embassy or consulate of the country you plan to visit to schedule an appointment for your visa application. Some countries allow you to apply for a visa online, while others require an in-person appointment.
- Submit your application: At your appointment, submit your visa application and supporting documents, and pay the visa fee (if applicable). You may also need to provide biometric data, such as fingerprints or a photograph.
- Wait for a decision: After you submit your application, the embassy or consulate will process your application and make a decision on your visa. This can take several weeks, so it's important to apply well in advance of your planned travel dates.
- Collect your visa: If your visa application is approved, you will need to collect your visa from the embassy or consulate. If your application is denied, you may be able to appeal the decision or reapply with additional supporting documents.
It's important to note that the visa application process can be complex and time-consuming, so it's recommended to start the process well in advance of your planned travel dates.
How Much Does a European Visa Cost?
The cost of a European visa can vary depending on the type of visa, the country you are applying to, and other factors. Generally, Schengen visas for short stays cost 80 euros for adults, and 40 euros for children between 6 and 12 years old. Some categories of travelers, such as students, researchers, and family members of EU citizens, may be eligible for reduced or waived visa fees.
It's important to note that visa fees are non-refundable, even if your visa application is denied. In addition to the visa fee, you may also need to pay for additional services, such as courier fees or translation services, depending on the requirements of the country you are applying to.
It's always a good idea to check with the embassy or consulate of the country you plan to visit for the most up-to-date information on visa fees and payment methods.
What is a Flight Itinerary for EU Visa Application?
A flight itinerary for an EU visa application is a document that outlines your travel plans, including your planned arrival and departure dates, flight numbers, and any layovers or connecting flights. The flight itinerary is not the same as a confirmed flight ticket, but it serves as proof that you have made travel arrangements and plan to leave the EU before your visa expires.
When applying for a Schengen visa, you may be asked to provide a flight itinerary as part of your visa application. This can be done by either booking a flight or creating a flight itinerary through a travel agency or online booking website. Some websites offer this service for free, while others may charge a fee.
It's important to note that a flight itinerary does not guarantee that you will be granted a visa, as there are many other factors that are taken into consideration when processing visa applications. However, providing a flight itinerary can help demonstrate your intention to travel to the EU for a specific period and can be helpful in obtaining a visa.
When creating a flight itinerary, be sure to include accurate information, including the correct flight dates, times, and airports. It's also a good idea to make sure that the flight itinerary aligns with the rest of your travel plans, including your accommodations and activities while in the EU.
What is Travel Insurance for Schengen Visa?
Travel insurance for Schengen visa is a type of insurance that provides medical and financial coverage for travelers visiting the Schengen area of Europe. It is a mandatory requirement for obtaining a Schengen visa for short-term stays.
The travel insurance policy must meet certain minimum requirements, including coverage for medical emergencies, hospitalization, and repatriation, with a minimum coverage of €30,000. The insurance policy must also be valid for the entire duration of your planned stay in the Schengen area and must be purchased from an approved insurance provider.
In addition to medical coverage, some travel insurance policies may also provide coverage for trip cancellation or interruption, baggage loss or delay, and other travel-related risks.
When applying for a Schengen visa, you will need to provide proof of travel insurance that meets the minimum requirements. This can be done by submitting a copy of your insurance policy along with your visa application.
It's important to note that travel insurance for Schengen visa is not just a requirement for obtaining a visa, but it's also a smart investment for protecting yourself against unexpected expenses and emergencies while traveling. Before purchasing a policy, be sure to review the terms and conditions carefully to ensure that it meets your needs and provides adequate coverage.
Does everybody need travel insurance?
Whether or not you need travel insurance depends on several factors, including your destination, the activities you have planned, and your personal circumstances. However, it's always a good idea to consider purchasing travel insurance for peace of mind and protection against unexpected events.
If you are traveling internationally, especially to countries with high medical costs, travel insurance can provide coverage for medical emergencies and treatment, as well as evacuation and repatriation. Additionally, travel insurance can cover other unforeseen events such as trip cancellation or interruption, lost or delayed baggage, and travel delays or interruptions.
Even if you have existing health insurance in your home country, it may not provide coverage while traveling abroad. Moreover, some countries may require proof of travel insurance before allowing entry, such as the Schengen area in Europe.
Ultimately, the decision to purchase travel insurance is a personal one based on your individual needs and circumstances. It's a good idea to carefully consider your options and choose a policy that provides the coverage you need for your specific travel plans.
How to Apply for a Schengen Visa Around the World?
To apply for a Schengen visa around the world, follow these general steps:
- Determine which Schengen country you will be visiting: The first step in the Schengen visa application process is to determine which Schengen country you will be visiting. You will need to apply for a visa from the embassy or consulate of that country.
- Gather the required documents: The next step is to gather all the required documents for your visa application. This may include your passport, visa application form, flight itinerary, travel insurance, financial documents, and any other supporting documents required by the embassy or consulate.
- Schedule an appointment: Once you have gathered all the required documents, you will need to schedule an appointment with the embassy or consulate of the Schengen country you will be visiting. You can do this by contacting the embassy or consulate directly or through their online appointment scheduling system.
- Attend the visa interview: On the day of your appointment, you will need to attend a visa interview at the embassy or consulate. During the interview, you will be asked questions about your travel plans, financial situation, and other details related to your visa application.
- Wait for the visa decision: After your interview, you will need to wait for the embassy or consulate to process your visa application. The processing time can vary depending on the country and the type of visa you are applying for. Once your visa has been approved, you will be able to pick it up from the embassy or consulate.
It's important to note that the specific requirements and procedures for Schengen visa applications may vary depending on the country you are applying to. Be sure to check with the embassy or consulate of the Schengen country you will be visiting for the most up-to-date information and instructions on how to apply for a visa.